What are PFAS?
More than 4730 compounds(1) belong to the group of PFAS (which stands for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances) that have been produced since the 1940s. Since these compounds do not originate from nature, the global pollution is the result of human activity. All PFAS are of anthropogenic origin. PFAS are "forever chemicals", chemicals that are very persistent in the environment and in the human body.
General structure of perand polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS)
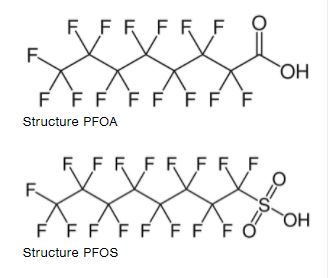
PFAS are organic compounds with a carbon chain in which hydrogen is substituted by fluorine. The carbon-fluorine bond is very strong which makes them “virtually indestructable“. The molecular structure of the PFAS provides them with non-sticky and tensid-like characteristics (because of their hydrophobic, lipophobic chain + hydrophilic head).There are polymers and non-polymers. Typical polymers are fluoropolymers, side-chain flurorinated polymers and perfluoropolyethers. Typical non-polymers are perfluoroalkyl acids (PFFFAs), perfluroalkane sulfonyl fluorides (PASF), perfluroalkyl iodides (PFAIs) and per- and polyfluroalkyl ether (PFPEs) based derivatives(2).
Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) have been the most produced and studied of these chemicals.
To cut a long story short: there are many different substance groups that need to be analyzed!

Where are PFAS used?
They are commonly used because of their non-sticky and tensid-like properties for various purposes:
- Textiles, textile coating, e.g., seat covers, carpets, outdoor clothing
- Fire extinguisher foams
- Food packaging, e.g., pizza cartons, paper cups
- Paper finishing
- Fibre coating
- Cookware
- Building material, e.g., water resistant lacquer
- Further consumer products, such as: furniture, polishing and cleaning agents and creams
How do PFAS find their way into the environment and the human body?
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) have been manufactured for more than 80 years, but health effects were neglected for a long time. In September 2020, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) published a new health risk assessment related to the presence of PFAS in food(3). This is the first EFSA expert opinion in which, in addition to PFOA and PFOS, other PFAS were also included in the exposure assessment and health risk assessment.
PFAS are emitted into the environment by different pathways. For example, exhaust air from industrial sources can contain PFAS and thus are dispersed into nearby ground and water bodies. Rain and snow, for example, can eventually carry them from the air into the soil and surface waters. Particle accumulation can even cause them to travel long distances through the air. PFAS are therefore also found far from industrial production sites and human living areas, such as in sediments from the Bering Sea to the Arctic(4/5). Through volatilization from products (evaporation from carpets or home textiles treated with soil-repellent agents) or from waterproofing sprays, indoor air can also be contaminated.
Soils can also be directly contaminated, for example by firefighting foams. With the uptake of PFAS from contaminated soils and waters in vegetation and their accumulation in fish, these substances enter the human food chain. Consequently, humans absorb PFASs from the environment through food, water or air.
These "forever chemicals" also find their way into wastewater treatment facilities from household sources. They then enter surface waters via treated wastewater or remain in sewage sludge. The sewage sludge, in turn, can be used as fertilizer in agriculture, and then over time these chemicals eventually leach into the groundwater. Once there, some of the precursor compounds are transformed into the persistent PFAS.


The new special phase – CHROMABOND PFAS
Over the years many different PFAS were developed. Now, they are found in the environment (water, food, soil, animals and humans) and their problematic health effects come into play.The challenge is that current analytical methods are limited.To tackle this challenge, we developed a special phase for the enrichment of a broad range of PFAS which provides good reproducibility and high recovery rates.
This is possible due to the different interactions the sorbent combination offers. These interactions are recommended by DIN 38407-42, EPA 537.1 and 533 guidelines.
Our CHROMABOND PFAS is a polymer-based combination phase which contains a weak anion exchange functionality. The combination of different SPE phases makes it possible to use various interactions (dipole-dipole, ionic, hydrophobic, H-bond).
CHROMABOND PFAS provides several advantages
- Solution for various PFAS substance classes
- > 28 PFAS can be enriched
- Sorbent retention mechanisms according to DIN 38407-42, EPA 537.1 and 533 guidelines
- High capacity
- High recovery rates
PFAS In Water

Read More - PDF Download
This application note shows the reliable and successful determination of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from drinking water with an optimized SPE method. By using CHROMABOND PFAS it is possible to achieve high recovery rates for PFAS from drinking water with good reproducibility. By the combination of different SPE sorbents in a multi-layer column it is possible to use various interaction types like ionic, hydrophobic, hydrogen bonds and dipole-dipole for the enrichment of a broad spectrum of PFAS. In this way, a SPE method could be developed with the strength of several directives EPA 537.1, EPA 533 and DIN 38407‑42.
PFAS From Textiles

Read More - Download PDF
This application note describes the determination of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from contaminated clothing. It demonstrates the extraction of PFAS from clothing samples using CHROMABOND PFAS column, a special SPE combination phase. The eluates are finally analyzed by HPLC-MS/MS.
PFAS In Contaminated Soil, sediments

Read More - PDF Download
This application note describes the determination of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) from contaminated soils. It demonstrates the extraction of PFAS from soil samples using CHROMABOND PFAS column, a special SPE combination phase, for the methodology described in DIN 38407‑42. The eluates are finally analyzed by HPLC-MS / MS.
Certified Reference Standards for PFAS Testing,
Available from Greyhound Chromatography


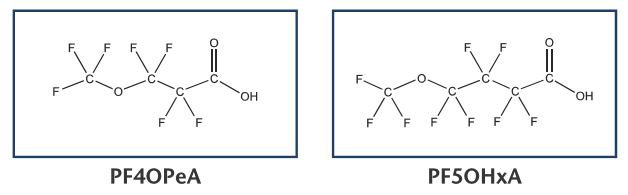
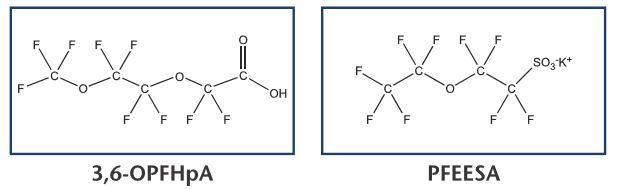
In response to the ever increasing demand for new Reference Standards to test for the presence of PFAS in everyday products Wellington Laboratories has increased its product line to include four new perfluoroether and perfluoropolyether-carboxylic acids (PF40PeA, PF50HxA, 3,6-0PFHpA and P5MeODIOXOAc), a perfluoroethersulfonate (PFEESA), perfluorodecanesulfonamide (FDSA-1) and N-methylperfluorobutanesulfonamide (N-MeFBSA-M).






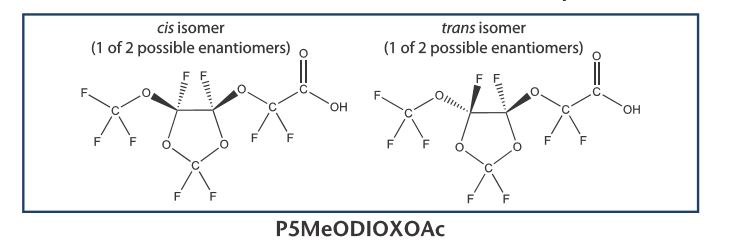









Greyhound Chromatography supplies an extensive range of pre-prepared and custom made Certified Reference Standards and Materials from a number of leading manufacturers, including British Pharmacopoeia (BP), Cerilliant (a Sigma Aldrich Company), Chem Service Inc., Chiron, European Pharmacopoeia (EP), Extrasynthese, High Purity Standards, Honeywell (Fluka), Laradon, NIST, Merck (Sigma Aldrich, Supelco) , Paragon Scientific, Pfaltz & Bauer, RTC (a Sigma Aldrich Company), United States Pharmacopoeia (USP), Wellington Laboratories.
Custom Mixtures manufactured by Chem Service Inc. and High Purity Standards to your specifications, fully certified to ISO 9001:2015 and accredited by ANAB to ISO/IEC 17025:2005 and ISO 17034:2016.
WELLINGTON REPORTER NOVEMBER 2019
PFAS Plastics Pollution of our Seas and Oceans

As the world wakes up to our environmental crisis it is important to note that every person living on our planet bears a responsibility for the world we have to live in. Resources are limited and their supply is thretened by overuse and careless disregard for how resources are produced and sustained. Whether it be our soil, air or water all are equally valuable is the quest to make our resources last and sustain our populations. Global contamination of our seas and oceans is only the tip of the iceberg. Today's research scientists bear an enormous responsibility as they endeavour to reduce and repair the impact we are having on our planet.
Greyhound Chromatography supplies the world's leading scientists with analytical reference standards and materials to ensure testing of contaminants in our environment to the highest level.
Latest Environmental News
Denmark just became the first country to ban PFAS from food packaging

Denmark will be the first country to ban PFAS Chemicals, which have been linked to cancer, elevated cholesterol and decreased fertility, from food packaging, starting next year.
PFAS substances, sometimes called "forever chemicals" because they don't break down in the environment, are used to repel grease and water in packaging for fatty and moist foods such as burgers and cakes.
What are PFAS chemicals, and what are they doing to our health?
"I do not want to accept the risk of harmful fluorinated substances (PFAS) migrating from the packaging and into our food. These substances represent such a health problem that we can no longer wait for the EU," Denmark's Food Minister Mogens Jensen said in a statement Monday.
PFAS chemicals are a family of potentially thousands of synthetic chemicals that are extremely persistent in the environment and in our bodies. PFAS is short for perfluoroalky and polyfluoroalkyl substances, and includes chemicals known as PFOS, PFOA and GenX.
They are all identified by signature elemental bonds of fluorine and carbon, which are extremely strong and what make it so difficult for these chemicals to disintegrate in the environment or in our bodies.
Under Denmark's new regulation, baking paper and microwave popcorn bags, for example, will be required to be manufactured without any PFAS.
"We congratulate Denmark on leading the way for healthier food and hope this will encourage similar action across the EU, the US and worldwide," said Arlene Blum of the Green Science Policy Institute and the Department of Chemistry at University of California, Berkeley.
FDA confirms PFAS chemicals are in the US food supply
"Given the potential for harm, we must ask if the convenience of water and grease resistance is worth risking our health," Blum said.
PFAS chemicals have been manufactured since the 1940s and can be found in Teflon nonstick products, stains and water repellants, paints, cleaning products, food packaging and firefighting foams.
These chemicals can easily migrate into the air, dust, food, soil and water. People can also be exposed to them through food packaging and industrial exposure.
A growing body of science has found that there are potential adverse health impacts associated with PFAS exposure, including liver damage, thyroid disease, decreased fertility, high cholesterol, obesity, hormone suppression and cancer.
In a statement, the Danish Veterinary and Food Administration said that the substances were very difficult to break down in the environment, and some of them accumulate in humans and animals.
The ban covers the use of PFAS compounds in food contact materials of cardboard and paper. The Danish government said it would continue to be possible to use recycled paper and paper for food packaging, but said PFAS compounds must be separated from the food with a barrier which ensures that they don't migrate into the food.
PFOS and PFOA are the two most-studied PFAS chemicals and have been identified as contaminants of emerging concern by the US Environmental Protection Agency.
PFOS was voluntarily phased out of production in the United States by 3M, the main manufacturer, starting in 2000. In 2006, PFOA began to be phased out as well. PFOA and PFOS are no longer manufactured or imported in the United States, but similar "replacement chemicals for PFOA and PFOS such as GenX, may be just as persistent," Susan M. Pinney, a professor in the Department of Environmental Health at the University of Cincinnati.
The European Food Safety Agency said it is reassessing the risks PFAS pose to human health and will report on its findings in the near future.
Wellington Laboratories offer a wide range of Certified Reference Standards for Testing and Analysis of Perfluorinated Compounds.
Perfluorinated Compounds (PFCs)
Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) are an emerging class of environmental contaminants. Their unique properties create a host of analytical challenges that require the use of native and mass-labelled standards for the generation of accurate data.
The most notable PFAS include PFOS (perfluorooctanesulfonate) and PFOA (perfluorooctanoic acid) and Wellington currently offers multiple mass-labelled standards for these compounds to meet your analytical needs. In fact, Wellington offers a large selection of native and mass-labelled per- and poly-fluorinated compounds, including:
- Perfluoroalkylcarboxylic Acids (PFCAs)
- Perfluoroalkylsulfonates (PFASs)
- Perfluorooctanesulfonamides (FOSAs)
- Perfluorooctanesulfonamidoethanols (FOSEs)
- Perfluorooctanesulfonamidoacetic acids (FOSAAs)
- Telomer Alcohols (FTOHs)
- Telomer Acids (FTAs)
- Telomer Sulfonates (FTSs)
- Perfluoroalkylphosphonic acids (PFAPAs)
- Perfluoroalkylphosphinic acids (PFPi’s)
Progress and Developments from Wellington Laboratories in 2019/2020
- New PFAS Mixtures and Solutions
About Wellington Laboratories
For more than 40 years Wellington Laboratories Inc. has been internationally recognised as a trusted source of high quality reference standard solutions for use in environmental/analytical testing and toxicological research. Wellington Laboratories offers an extensive inventory of individual certified reference standards and solution mixtures of native and mass-labelled halogenated organic compounds including polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorinated dibenzofurans, polychlorinated biphenyls, halogenated flame retardants and perfluorinated compounds. Wellington Laboratories also offer a variety of calibration sets and support solutions designed to be used for common regulatory methods or modified in-house methods.
Wellington’s Reference Standards are used mainly in Environmental/analytical testing and toxicological research. Wellington offers an extensive inventory of individual certified reference standards and solution mixtures of native and mass-labelled halogenated organic compounds including polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, polychlorinated dibenzofurans, polychlorinated biphenyls, halogenated flame retardants and perfluoronated compounds. Wellington also offer a variety of calibration sets and support solutions designed to be used for common regulatory methods of modified in-house methods.
Wellington Laboratories are committed to the distribution of quality products as well as the maintenance of excellent customer service. In fact, in order to provide your customers with the best possible service, Wellington have three ISO certifications (ISO 9001:2008, ISO/IEC 17025:2005, and ISO Guide 34:2009) which cover all aspects of planning, production, testing, distribution, and post-distribution service. These certifications allow Wellington Laboratories to monitor and maintain the highest level of quality and service and also allow their customers to satisfy the requirements of their own ISO certifications.
Wellington’s ISO/IEC 17025:2005 accreditation has been certified by the Canadian Association for Laboratory Accreditation Inc. (CALA) the scope is available for review on the CALA Directory of Accredited Laboratories (http://www.cala.ca).
Similarly, Wellington’s ISO Guide 34:2009 accreditation has been certified by ANSI-ASQ National Accreditation Board (ANAB), the certificate and scope are available on their website (http://anab.org/).
We are able to supply hard copies of any of the ISO certificates for yourself and your customers.

Wellington Laboratories Catalogue 2021 - 2023

Wellington Laboratories is pleased to announce the long-awaited release of their latest catalogue which contains the most up-to-date-listing of Wellington's Certified Reference Standard Solutions, Solution/Mixtures and Calibration Sets. Below you will find a selection of new products introduced in this new catalogue. Amongst the new products on offer you will find a comprehensive calibration set for polychlorinated naphthalenes (PCNs), native and mass-labelled PCN Support Solutions and additional individual organochlorine pesticide (OPC) standards.
Wellington Laboratories also continue to offer most of the products that were listed in their previous catalogue as they have remained relevant for environmental analysis and are frequently requested.
NEW ADDITIONS TO WELLINGTON LABORATORIES PRODUCT LIST
Alternative Method 16130 Calibration Set (16130CVS)
Mass-Labelled PCDD Window Defining Mixture (MD5CWDS)
Mass-Labelled PCDF Window Defining Mixture (MF5CWDS)
35 Individual Native OCP Standards
24 Mass-Labelled OCP Standards
PCN Calibration Set (PCN-CVS-A) & Support Solutions
27 Individual Native PCN Standards
14 Mass-Labelled PCN Standards
and more .........
Greyhound Chromatography is pleased to represent Wellington Laboratories throughout Europe and the Middle East. Our Sales team will be delighted to deal with your enquiry for Wellington products. Email: sales@greyhoundchrom.com
Full Range of Wellington Laboratories' Products
PFAS and Other Toxic Forever Chemicals in Drinking Water

For over 30 years the European Union have worked tirelessly to protect the integrity of our drinking water. EU officials have recently reached a provisional agreement to update the Union's 1998 Drinking Water Directive to tighten up the permissible limits allowed for both PFAS and several other drinking water contaminants, including bisphenol-A, microplastics, lead and chromium. The at the time of writing the European Parliament and Council are still to formally approve the proposal.
European drinking water standards currently far exceed the standards set in the United States but this is a changing picture as state by state new instances of contaminants are emerging. Currently, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has only issued a nonenforceable health advisory of 70 ppt for PFOA, formerly used by DuPont to make Teflon, and PFOS, formerly an ingredient in 3M’s Scotchgard. Those compounds are no longer manufactured in the U.S., but they and other PFAS contaminate the drinking water for an estimated 110 million Americans. PFOA, PFOS and some other PFAS chemicals have been linked to cancer, thyroid disease, reproductive and immune system problems, and other health harms.
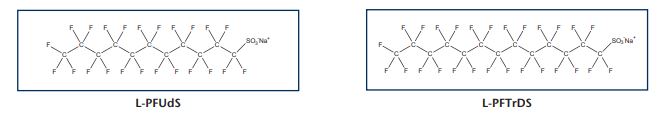
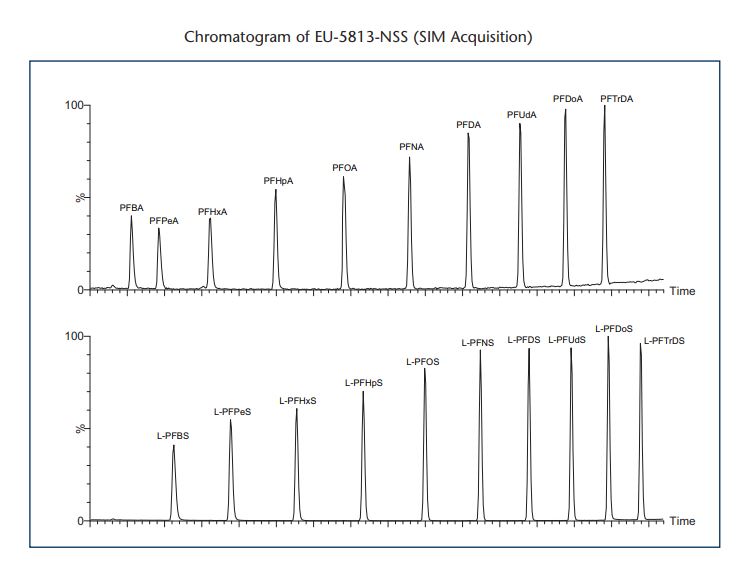
The european Parliament and the Council of the European Union have released new requirements for the analysis of per- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water intended for human consumption (5813/20). This amendment to Council Directive 98/83/EC included perfluoroalkanesulfonates that are not commercially available. In response to this Wellington Labroatories, Canada, is pleased to announce that its chemists have synthesized, purified, characterized and prepared accurate certified reference standards of the required substances: sodium perfluoro-1-undecanesulfonate (L-PFUds) and sodium perfluoro-1-tridecanesulfonate (L-PFTrDS). Wellington Laboratories have also prepared a native solution/mixture (EU-5813-NSS) that contains all of the PFAS listed in the drinking water directive (5813/20) for your convenience. This solution/mixture can be used in conjunction with two of Wellington's existing mass-labelled PFAS mixtures to easily prepare a calibration set for quantification.
Suggested extraction standard mixture : MPFAC-C-ES
Suggested injection standard mixture: MPFAC-C-IS



Q-Range PFAS Analysis Screw Top Vials Kits, 9mm
Please visit our website www.greyhoundchrom.com to view all available vials and accessories.
Ordering Information:
You can order on-line (registration required), www.greyhoundchrom.com
or by telephone, +44 (0)151 649 4000 - Sales Department
Request a quotation: sales@greyhoundchrom.com
General Information: info@greyhoundchrom.com